Bloom's Taxonomy
Bloom's taxonomy, Taxonomy of educational objectives, developed in the 1950s by the American educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom.Bloom's taxonomy fostered a common vocabulary for thinking about learning goals. It engendered a means of aligning educational goals, curricula, and assessments, and it provided a structure for instructional activities and curriculum.

Wat is de taxonomie van Bloom? agile4all
To provide learners with clearer instructional goals, a group of researchers led by Bloom's colleague David Krathwohl and one of Bloom's students, Lorin Anderson, revised the taxonomy in 2001. In the new variant, nouns were replaced by action verbs. Also, the two highest levels of the taxonomy were swapped. The new learning stages are.

A 3 Dimensional Model Of Bloom's Taxonomy Blooms taxonomy, Learning objectives, Learning theory
Leerdoelen en de taxonomie van Bloom (Nederlandse tekst) When teaching, it is important to ask yourself what exactly you want your students to learn. Which subjects do you want to cover, at what level should students master these subjects, and is knowledge the main focus or specific skills, or a combination of both? The learning goals determine.
/5857112597_eae735e2af_o-58ac97533df78c345b72a141.jpg)
How to Construct a Bloom's Taxonomy Assessment
A Brief History of Bloom's Taxonomy. This model was originally developed in the 1950s and 60s by a group of researchers led by educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom—a model that became known as "Bloom's Taxonomy.". Bloom's work was revised in 2001 by another group of researchers led by Lorin W. Anderson, a former student of Bloom.

Taxonomie van Bloom Schoolupdate academie
In 2001 Bloom's taxonomy was revised by a group of cognitive psychologists, led by Lorin Anderson (a former student of Bloom). To update the taxonomy to reflect 21st century work the authors used verbs to re-label the six categories and included "action words" to describe the cognitive processes by which learners encounter and work with.

Taxonomie Van Bloom
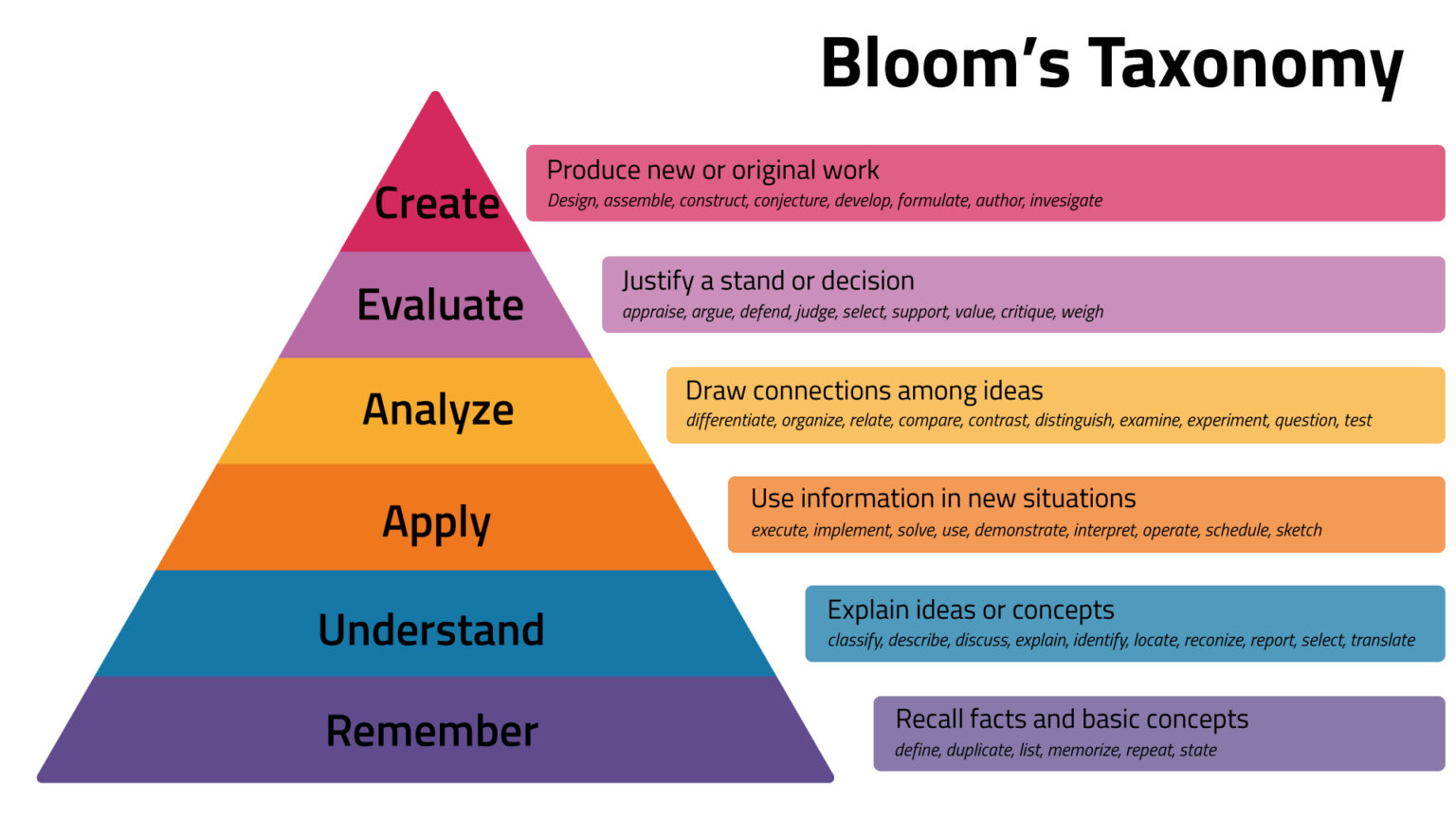
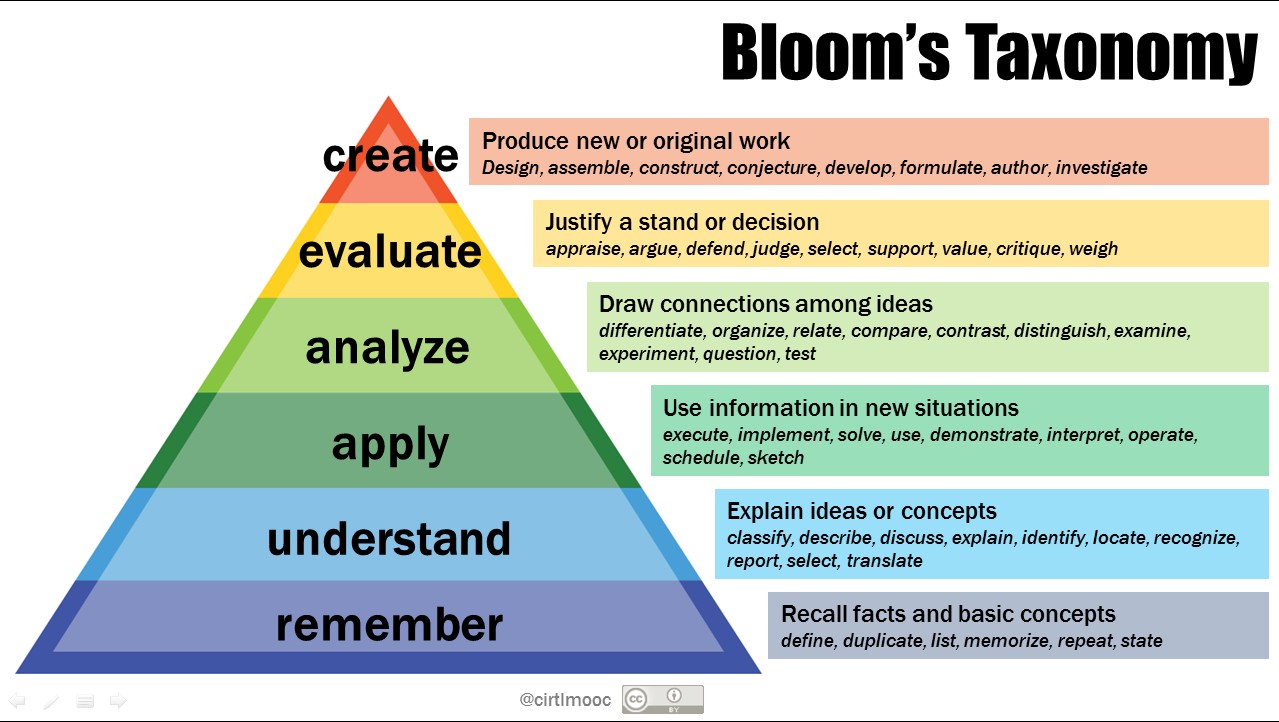
The original Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, commonly referred to as Bloom's Taxonomy, was created by Benjamin Bloom in 1956, and later revised in 2001. Bloom categorized and classified the cognitive domain of learning into varying levels according to complexity and richness. As you travel up the pyramid, the level of complexity increases.
Taxonomie de Bloom, formation et Réalité Virtuelle ? Eureka ! WiDiD
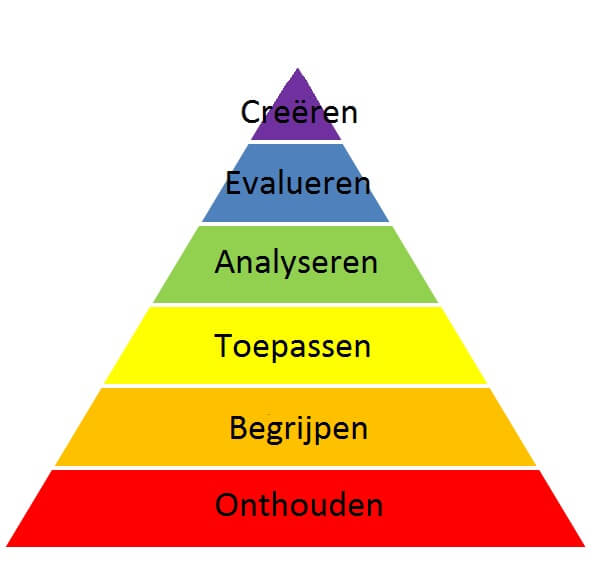
De taxonomie van Bloom is een van de meest gebruikte manieren om verschillende kennisniveaus in te delen. De onderwijspsycholoog Benjamin Bloom bedacht deze taxonomie als algemeen model voor de doelstellingen van het leerproces. De taxonomie van Bloom onderscheidt zes niveaus, die oplopen in moeilijkheidsgraad: Onthouden. Begrijpen.
Optimaliseren van leerrendement De (aangepaste) taxonomie van Bloom Haagse Hoogvliegers
Bloom's taxonomy is a classification system used to define and distinguish different levels of human cognition—i.e., thinking, learning, and understanding. Educators have typically used Bloom's taxonomy to inform or guide the development of assessments (tests and other evaluations of student learning), curriculum (units, lessons, projects, and other learning activities), and.

Taxonomie Van Bloom
Bloom's taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used for classification of educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. The three lists cover the learning objectives in cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains. The cognitive domain list has been the primary focus of most traditional education and is frequently used to structure curriculum learning.

Blooms Taxonomy Educationsupportuk
This post is by Ron Berger, Chief Academic Officer at EL Education. Almost every educator knows the Bloom's Taxonomy cognitive framework. The related pyramid graphic has influenced curriculum.

Taxonomia De Bloom Infografias Teaching English Pedagogy Teaching Images
In the revised taxonomy, knowledge is at the basis of these six cognitive processes, but its authors created a separate taxonomy of the types of knowledge used in cognition:

Taxonomie van bloom uitleg denkvaardigheden
Bloom's Taxonomy. Bloom's Taxonomy categorizes skills that students are expected to attain as learning progresses. Originally published in 1956, the tool is named after Benjamin Bloom, who was the Associate Director of the Board of Examinations at the University of Chicago. Now a classic arrangement of intellectual skills, the taxonomy and.

Wat is de taxonomie van Bloom? agile4all
Learning outcome examples adapted from, Nelson Baker at Georgia Tech: [email protected]. How Bloom's works with Quality Matters. For a course to meet the Quality Matters standards it must have learning outcomes that are measurable. Using a verb table like the one above will help you avoid verbs that cannot be quantified, like: understand, learn, appreciate, or enjoy.
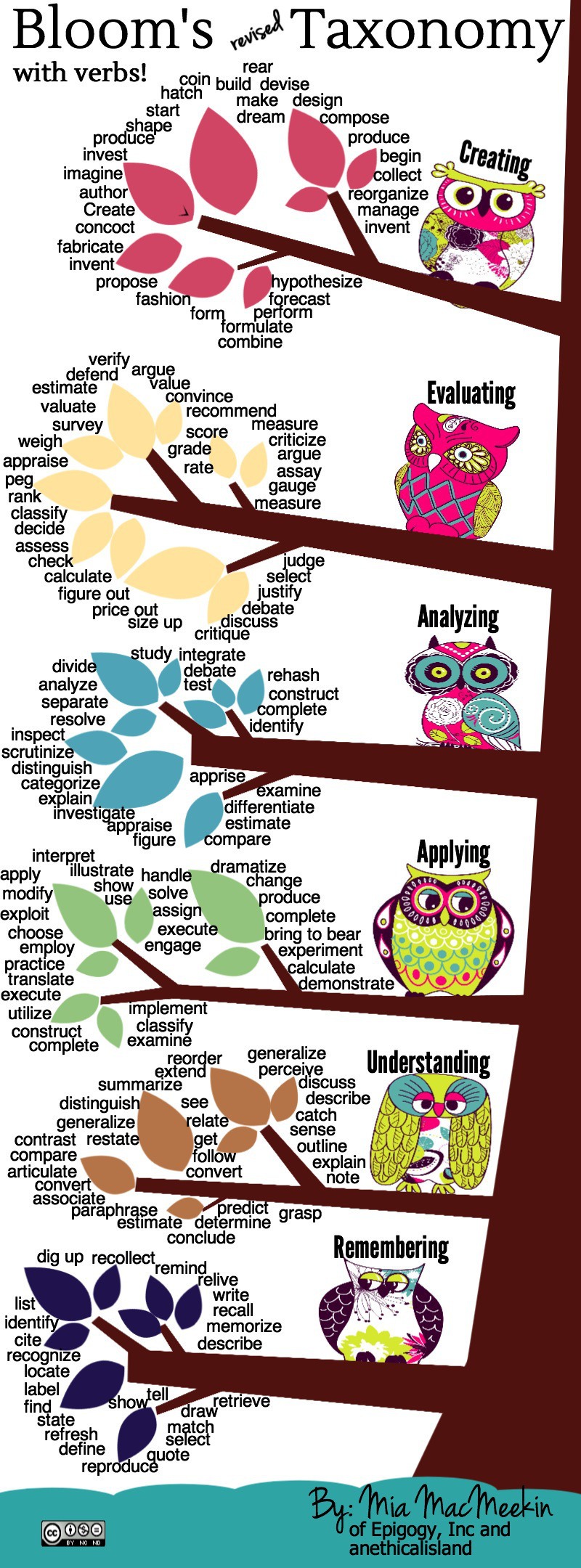
Bloom's Revised Taxonomy Action Verbs infographic eLearning Infographics
Bloom's Taxonomy is actually a set of three different models, exploring three separate aspects (or "domains") of thinking and learning. These domains are: Cognitive - knowledge-based learning. Affective - emotional learning, including how we handle feelings and develop attitudes. Sensory - physical learning: sensing, moving and manipulating.
10. Blooms taxonomy Andrea´s Portfolio
In 1956, Benjamin Bloom with collaborators Max Englehart, Edward Furst, Walter Hill, and David Krathwohl published a framework for categorizing educational goals: Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. Familiarly known as Bloom's Taxonomy, this framework has been applied by generations of K-12 teachers and college instructors in their teaching.
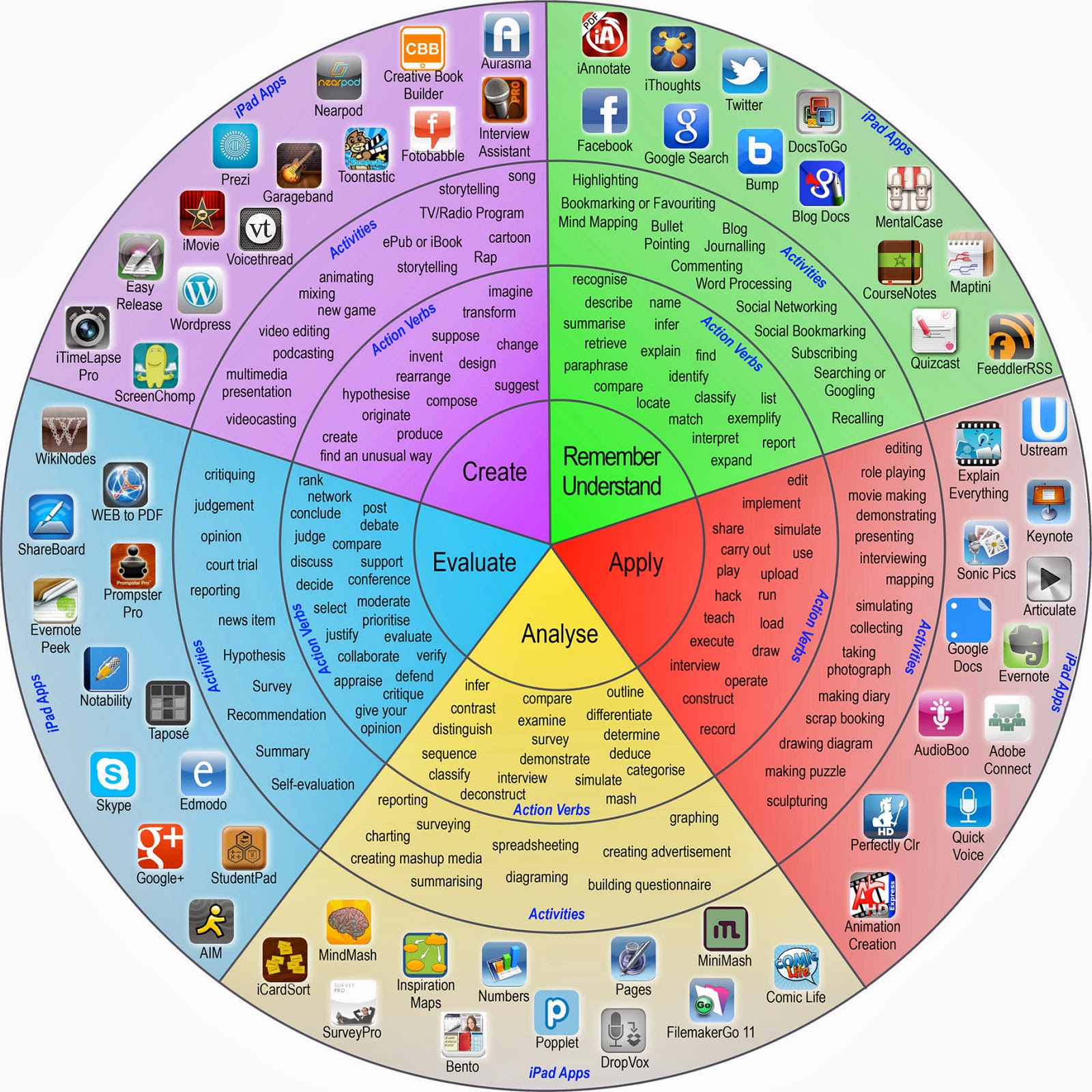
Blooms Taxonomy Infographic Taxonomia De Bloom Taxonomia De Marzano Images
A group of cognitive psychologists, curriculum theorists and instructional researchers, and testing and assessment specialists published in 2001 a revision of Bloom's Taxonomy with the title A Taxonomy for Teaching, Learning, and Assessment. This title draws attention away from the somewhat static notion of "educational objectives" (in.