
Difference Between Plasmolysis and Turgidity Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms
Turgor pressure allows plants to stay firm and erect, and plants without turgor pressure (known as flaccid) wilt. A cell will begin to decline in turgor pressure only when there is no air spaces surrounding it and eventually leads to a greater osmotic pressure than that of the cell. [1]

Practicum Plasmolyse en turgor bij plantencellen
We found turgor pressure to be 0.18±0.08MPa (mean±standard deviation) for cells in 0.2M solution and 0.54±0.15MPa for cells in water (Fig. 2F). These values are consistent with the range of turgor pressures that has been reported for larger plant cells using a pressure probe ( Tomos and Leigh, 1999 ) but ~50 % smaller than estimates that.

Osmose turgor en plasmolyse bij planten Kruidachtige en
Three terms—hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic—are used to describe whether a solution will cause water to move into or out of a cell: If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, there will be a net flow of water out of the cell, and the cell will lose volume. A solution will be hypertonic to a cell if its solute concentration is higher.
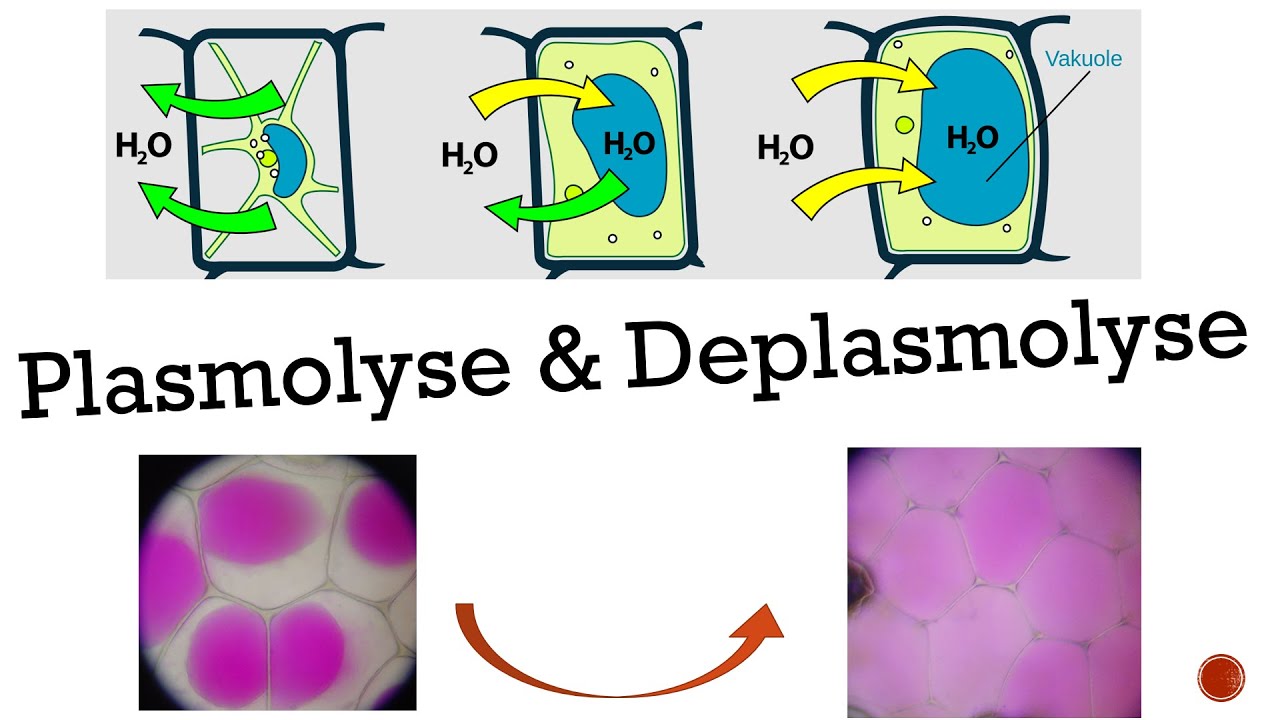
Plasmolyse & Deplasmolyse [Biologie, Oberstufe] YouTube
The loss of turgor causes the violent detachment of the living protoplast from the cell wall. The plasmolytic process is mainly driven by the vacuole. Plasmolysis is reversible (deplasmolysis) and characteristic to living plant cells. Obviously, dramatic structural changes are required to fulfill a plasmolytic cycle.

Understanding Plasmolysis How Plant Cells Lose Turgor Pressure › Don Antonio Lugo High School Band
Turgid leaf cell (turgor about 0.5 MPa) and flaccid cell (zero turgor) that has lost some water. With further water loss, the cell collapses. The collapse of the wall is called cytorrhysis. Plasmolysis occurs when a cell is placed in a solution of osmotic strength greater than that of the cell.
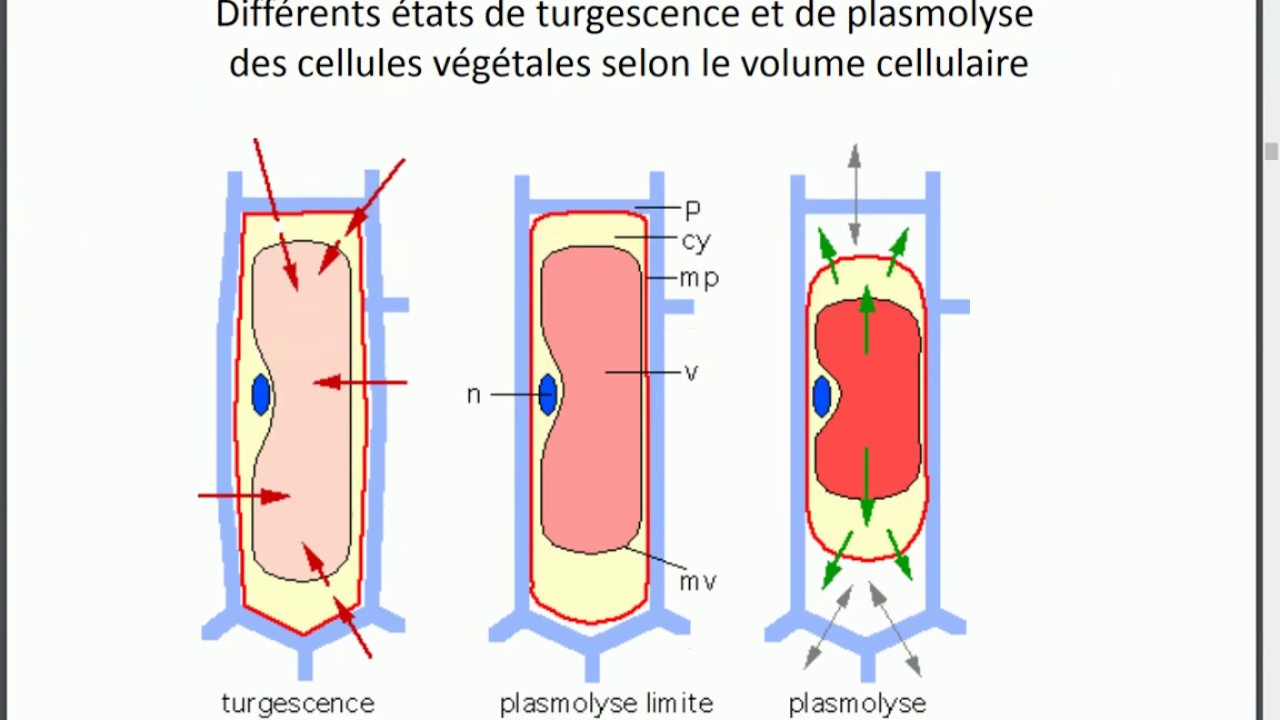
turgescence et plasmolyse PARTIE 7 YouTube
The loss of turgor causes the violent detachment of the living protoplast from the cell wall. The plasmolytic process is mainly driven by the vacuole. Plasmolysis is reversible (deplasmolysis) and characteristic to living plant cells. Obviously, dramatic structural changes are required to fulfill a plasmolytic cycle.
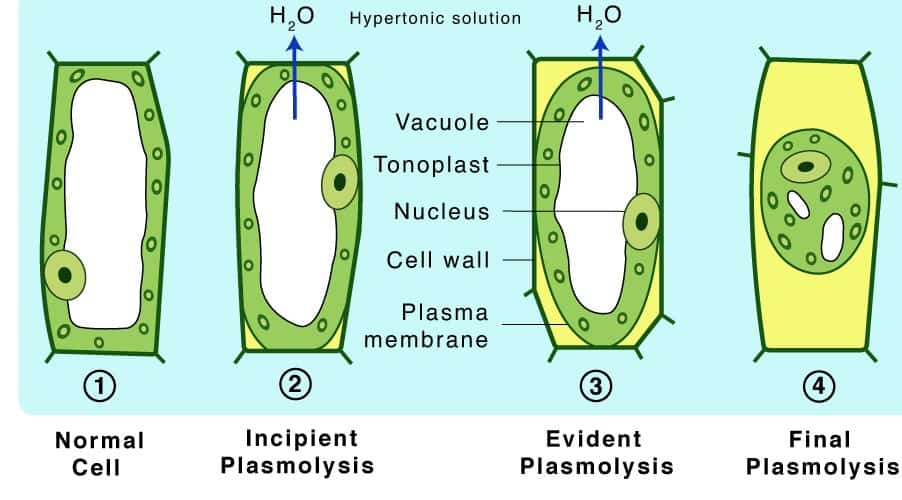
Plasmolysis in a cell examples, importance, and types
Plasmolysis Definition. Plasmolysis is when plant cells lose water after being placed in a solution that has a higher concentration of solutes than the cell does. This is known as a hypertonic solution. Water flows out of the cells and into the surrounding fluid due to osmosis. This causes the protoplasm, all the material on the inside of the.

Osmose, turgor, plasmolyse, grensplasmolyse YouTube
Schimmels en bacteriën plasmolyseren dan. Tegenovergesteld aan plasmolyse is turgor, als de omgeving een lagere osmotische waarde heeft en de cel veel water opneemt. De cel zwelt op en drukt tegen de celwand, dit verleent de cel zijn stevigheid. Wanneer de wanddruk gelijk is aan de turgordruk, is de cel turgescent.
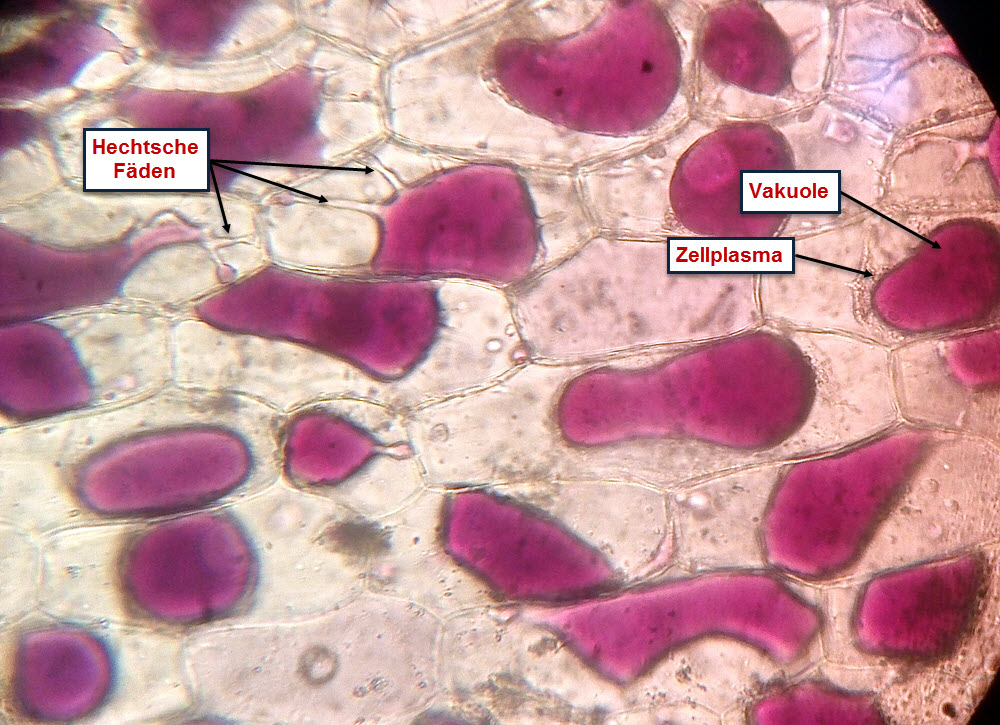
Plasmolyse Bioclips.de
Turgor en plasmolyse, de rol van osmose in celstevigheid HAVO/VWO juf Aminozuur 5.73K subscribers Subscribe 7.8K views 3 years ago Cellen 4 HAVO/VWO In deze video leg ik uit wat turgor en.

Osmose turgor en plasmolyse bij planten Kruidachtige en
Plasmolysis is a typical response of plant cells exposed to hyperosmotic stress. The loss of turgor causes the violent detachment of the living protoplast from the cell wall. The plasmolytic.

turgor plasmolyse YouTube
Observing osmosis, plasmolysis and turgor in plant cells Class practical or demonstration A single layer of plant cells is placed on a microscope slide and either distilled water or 5% sodium chloride solution is added to the cells. Osmosis will occur resulting in either turgid cells or plasmolysed cells. Lesson organisation
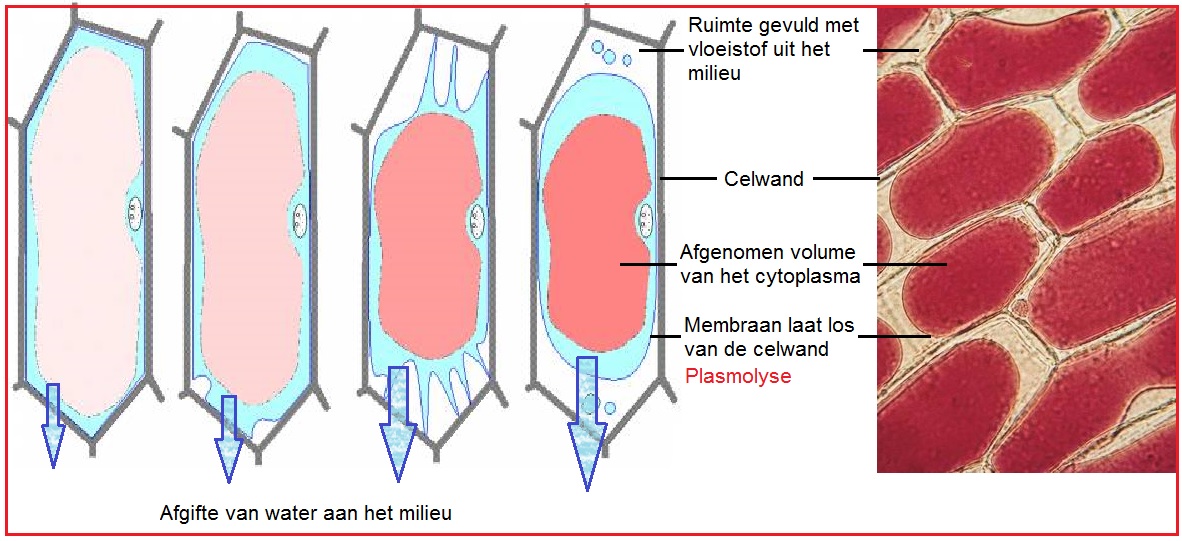
Plasmolyse
Metabolomics (2019) Scientists have identified turgor-based actuation as a fundamental mechanism in plant movements. Plant cell turgor is generated by water influx due to the osmolyte.

PPT Osmose bij planten PowerPoint Presentation ID2180400
Introduction Plasmodesmata are channels that traverse the cell walls and create symplasmic continuity. They have been shown to play a key role in the mobilization of different types of molecules such as hormones, sucrose, transcription factors, and viruses ( De Storme and Geelen, 2014; Sager and Lee, 2014; Han and Kim, 2016 ).

Difference Between Plasmolysis and Cytolysis Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms
The loss of turgor causes the violent detachment of the living protoplast from the cell wall. The plasmolytic process is mainly driven by the vacuole. Plasmolysis is reversible (deplasmolysis) and characteristic to living plant cells. Obviously, dramatic structural changes are required to fulfill a plasmolytic cycle.
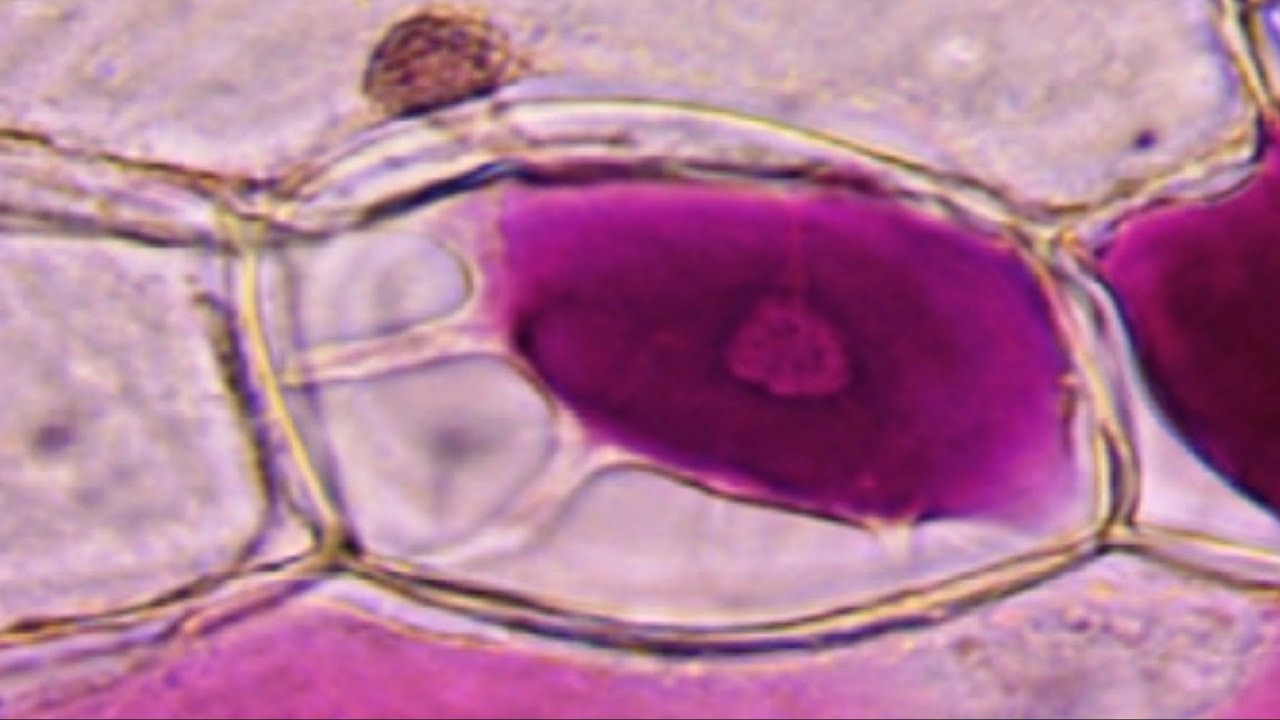
Plasmolyse vs déplasmolyse avec éclatement de la membrane cytoplasmique SVT Kempf Elorn YouTube
Turgor pressure is the pressure applied by the excess cell sap on the cell wall. Plasmolysis is the phenomenon of exosmosis of cell sap. It means that the cell sap escapes the protoplast and causes shrinkage of the cell. This happens whenever water moves out of the cell. This causes the turgor pressure to be reduced in the cell as it becomes flaccid.

presión del turgor. Ósmosis de células vegetales. Ilustración vectorial Imagen Vector de stock
Plasmolysis is a typical response of plant cells exposed to hyperosmotic stress. The loss of turgor causes the violent detachment of the living protoplast from the cell wall. The plasmolytic process is mainly driven by the vacuole. Plasmolysis is reversible (deplasmolysis) and characteristic to living plant cells.